California got its name from an expedition led by Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo in 1542. It is thought that the members of the expedition, which sailed from the southern tip of Mexico northward, got the name “California” from a 1510 Spanish novel, which talked about an idyllic fictional island by that name. Now the state is known by many names, including “the Golden State.”
That name, which is the state’s official nickname, was coined due to the role the gold rush played in California becoming the 31st state on September 9, 1950. Although, some people think that “golden” refers to the states crop fields or sunshine. The State of California became a territory in 1847 when Mexico surrendered it to John C. Frémont.
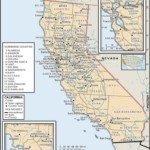
California Counties – The State of California was created as the 31st state on September 9, 1850. It has 58 Counties. The State of California is bordered by Oregon, Nevada, Arizona. The capital is Sacramento and the official state website is http://www.ca.gov/.
Select a California county to view information & records pertaining to each County
California Genealogy Record Guides
Getting Started with California Genealogy and Family Trees
California genealogy is a popular hobby as well as a lucrative business. You may be looking for a way to trace your family history and ancestry, or searching for genealogy records for someone else. Either way, this can be a difficult but rewarding task. There are some tricks and tips you can use to improve your searches when you are looking for documentation to help with your genealogy records.
- California’s records are fairly complex, due in part to the nature of how counties were formed.
- Vital records in California have been kept by the state registrar of vital statistics since 1 July 1905. Earlier vital records are entered in the county where the event took place.
- Divorce records are available in the office of the clerk of the superior court in the county in which the proceedings were conducted.
- Censuses were taken for the following missions: San Carlos (1796), San Luis Obispo (1797, 1798), San Antonio (1798), and Soledad (1798).
- The California Constitution of 1849 provided for a census of the state population in the years 1852 and 1855 and each succeeding ten years thereafter. A few cities and towns have special censuses for California through the twentieth century
- The earliest land records relate to the Spanish (1769–1822) and Mexican (1822–48) eras and are mostly in Spanish.
- The court that has jurisdiction over an estate is the superior court in the county in which the person resided at the time of his or her death.
- Each of Californias four levels of jurisdiction: the municipal court, the superior court, the six district courts of appeal and the state supreme court, has a clerk of the court.
- Printed secondary sources of transcribed cemeteries exist for most California counties.
- The California State Archives has become the state’s official repository for service records of Californians from the Indian Wars through the World Wars, including National Guard records.
- California provided several ports and points of entry for immigrants.
- Prior to 1906 a person might have filed for naturalization in any court in the state; for this time period, there are no guides for locating a naturalization in the state other than for those records that were entered at federal district court.
California Genealogy Databases and other Helpful Links
Lastly, websites such as those listed below will provide state-specific genealogical details that can work wonders for California genealogy enthusiasts: